electronic configuration of cr3|Electron Configuration Chart of All Elements (Full Chart) : Clark We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since . Learn how to draw a cute custom Blastoise Squishmallow! This is an easy step-by-step lesson great of all ages and kids for cute Blastoise. #howtodraw #Blasto.
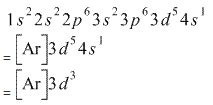
electronic configuration of cr3,How to Write the Electron Configuration for Chromium (Cr, Cr2+, and Cr3+) In order to write the Chromium electron configuration we first need to know the number of electrons for the Cr atom (there are 24 electrons). Once we have the configuration for Cr, the ions are .Both of the configurations have the correct numbers of electrons in each orbital, it is .
Therefore the N electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. Video: Nitrogen .
Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for magnesium go in .We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since .
Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for sodium go in the 2s .
Lithium is the third element with a total of 3 electrons. In writing the electron .How to Write the Electron Configuration for Boron. Boron is the fifth element with a .
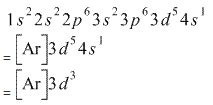
Transition elements have electrons in the d orbital, which introduces some additional nuance in the electron configurations. First, recall that the n = 3 shell is the .Calculate the number of unpaired electrons in the following gaseous ions: Mn3+, Cr3+, V3+ and Ti3+ asked Dec 23, 2017 in Chemistry by sforrest072 ( 130k points) d-and f- block elementsElectronic configuration of Cr 3 + Cr is an exception where the last electron enters into the 3d orbital instead of 4s orbital to attain half-filled stability. The electronic configuration of . To write the configuration for the Chromium ions, first we need to write the electron configuration for just Chromium (Cr). We first need to find the number of electrons for the Cr atom (there. Mar 23, 2023 Six electrons will be placed in the 2p orbital as the p orbital has a maximum capacity of six, followed by the 3s orbital with two electrons. We’ll shift to the 3p to insert the following .electronic configuration of cr3The electronic configuration of C r (24) atom is: 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 2 3 p 6 4 s 1 3 d 5 which is half-filled d-orbital. C r 3 + has 3 electrons removed from the outermost shell.
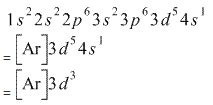
The element with electronic configuration [xe] 54 4f 14 5d 1 6S 2 belongs to Electronic configuration of manganese (Z = 25) is ______ Explain the observation, at the end of each period, there is a slight increase in the atomic radius of d-block elements.
The energy of an electron in the 3rd orbit of hydrogen atom is –E. The energy of an electron in the first orbit will be. Define orbital? what are the n and l values for 3p x and `"4d"_("x"^2 - "y"^2)` electron? Calculate the uncertainty in position of an electron, if Δv = 0.1% and υ = 2.2 × 10 6 ms-1As a result, one of the 4s 2 electrons moves to the 3d 5, which fills it halfway. Thus, we have the (correct) configuration of Cr: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 5 4s 1. For the electronic configuration of the Cr 3+ ion, we will remove three electrons from the Cr (one from the 4s 1 and two from the 3d 5 ), leaving us with 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3 6 .
Hence, there are 3 unpaired electrons in Cr3+. Was this answer helpful? 17. Similar Questions. Q 1.Write electronic configuration for Cu, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cr3+. Write the electronic configuration of Cu2+ ion. [Cu =29] Write down the electronic configuration of:(i) Cr^3+(iii) Cu^+(v) Co^2+(vii) Mn^2+(ii) Pm^3+(iv) Ce^4+(vi) Lu^2+(viii) Th^4+📲PW App Link - https://bit.ly/PW. Electron Configuration Chart of All Elements (Full Chart) March 23, 2023 Jay. View all posts. Jay. Electron configuration chart of all Elements is mentioned in the table below. The Shorthand electron configuration (or Noble gas configuration) as well as Full electron configuration is also mentioned in the table. Atomic no.An atomic cation with a charge of +1 has the following electron configuration: (Ar) 4s^2 3d^{10} 4p^1. How many 4s electrons are in the ion? An atomic cation with a charge of +1 has the following electron configuration: (Ar) 4s^2 3d^{10} 4p^1. How many electrons does the ion have? Determine the total number of valence electrons in SO_4^{2-}. While acting as a reducing agent, it gets oxidized to Cr3+ (electronic configuration, d3). This d3 configuration can be written as configuration, which is a more stable configuration. In the case of Mn3+ (d4), it acts as an oxidizing agent and gets reduced to Mn2+ (d5). This has an exactly half-filled d-orbital and is highly stable.
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron .
Assertion. Electronic configurations of C r3+ (containing 21 electrons) is same as that of S c(Z = 21), i.e., isoelectronic species have the same electronic configuration. Reason. Orbitals of atoms as well as ions are filled in order of increasing energy following aufbau principlea. If both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the true .
The same rule will apply to transition metals when forming ions. You should note that the ns electrons are always lost before the (n-1)d when forming cations for transition metals.For example, the electron configuration for Zn: [Ar]4s 2 3d 10 . the electron configuration for Zn +2: [Ar]3d 10 . The transition metals still do not end up being isoelectronic with a .
electronic configuration of cr3 Electron Configuration Chart of All Elements (Full Chart) Electronic configurations of `Cr^(3+)` (containing 21 electrons) is same as that of `Sc (Z = 21)`, i.e., isoelectronic species have the same electronic configuration Reason. Orbitals of atoms as well as ions are filled in order of increasing energy following aufbau principle A. If both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the true .
Write the electron configurations of these cations. Solution. First, write the electron configuration for the neutral atoms: Zn: [Ar]3 d10 4 s2. Cr: [Ar]3 d5 4 s1. Next, remove electrons from the highest energy orbital. For the transition metals, electrons are removed from the s orbital first and then from the d orbital.
Electron Configuration Chart of All Elements (Full Chart)Write down the number of 3d electrons in each of the following ions: Ti , V , Cr , Mn , Fe , Fe , CO , Ni and Cu . Indicate how would you expect the five 3d orbitals to be occupied for these hydrated ions (octahedral). Write down the electronic configuration of Cr 3+P m 3+Cu +Ce 4+Co 2+Lu 2+Mn 2+Th 4+. For example, the electron configurations of the transition metals chromium (Cr) and copper (Cu), are not those we would expect. Rather, Cr and Cu take on half-filled and fully-filled 3d configurations. The electron configuration of chromium (Cr) includes a half-filled 3d subshell. Cr: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3 s 2 3p 6 4s 1 3d 5CHROMIUM(III) oxidation state chemistry Chromium forms the stable hexaaquachromium(III) ion, [Cr(H 2 O) 6] 3+ (aq). Electron configuration of the Cr 3+ ion is [Ar]3d 3. The colour appears violet-blue-grey (some texts say red-violet?), but often looks green when produced in reactions, especially if chloride ions are present that can act as .
electronic configuration of cr3|Electron Configuration Chart of All Elements (Full Chart)
PH0 · Write down the electronic configuration of: (i) Cr3
PH1 · What is the electron configuration of Cr 3+? Chemistry Q&A
PH2 · What is the electron configuration of Cr 3+? Chemistry Q&A
PH3 · What is the electron configuration of Cr 3+?
PH4 · What is the electron configuration of Cr
PH5 · What is the Electron Configuration of Cr3+
PH6 · The electronic configuration of { Cr }^{ 3+ } is:left[ Ar right] { 3d
PH7 · The electronic configuration of { Cr }^{ 3
PH8 · Electron Configuration for Cr, Cr2+, and Cr3
PH9 · Electron Configuration for Chromium (Cr, Cr2+, Cr3+)
PH10 · Electron Configuration for Chromium (Cr and Cr2+, Cr3+ ions)
PH11 · Electron Configuration Chart of All Elements (Full Chart)
PH12 · Chromium (Cr)
PH13 · 1.9: Electron Configurations for Transition Metal Elements